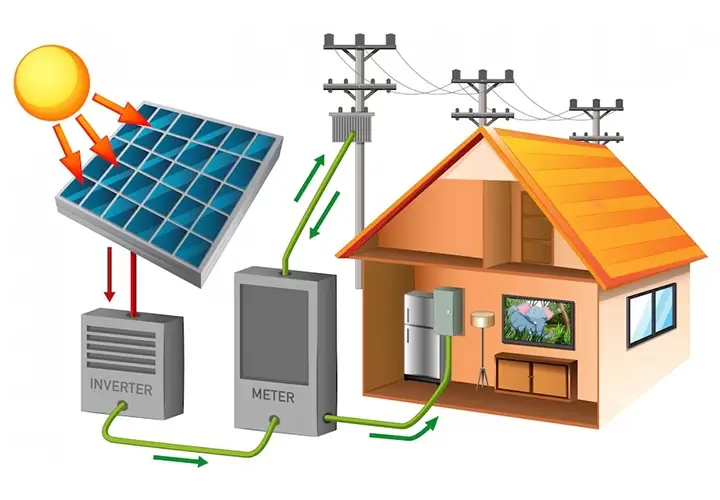
With a Rooftop Solar Panel for Home, you can do more than just green and sustainable energy. Your solar system may produce a lot of energy, much of which is not required to run your house, which is deemed wasted. Net metering solves this issue by connecting your system to the utility grid. This enables you to return the excess power to the grid for increased benefits. In this blog, we have focused on how net metering works and the advantages it brings along:
What is Net Metering?
Net metering is a system the utility boards use to measure the energy used and send it back to your system. If your residence is metered, it provides a bill according to your energy usage at night, depending on the excess energy required and produced by your PV system.
How Does Net Energy Metering Work?
When you use power from the grid, the meter records this usage with a spin. Similarly, when you return excess power to the grid, the meter records this by spinning in the opposite direction. This recording by the meter gives the final electricity bill.
If you are not already affiliated with this system, you need to connect your photovoltaic system to the grid which may require special equipment that your local solar system provider offers.
What are the Requirements for Net Metering?
Different locations have different systems; hence, their prerequisites also vary accordingly. National programs have various regulations for hybrid rooftop solar systems being connected to the grid depending upon:
- the extent to which credits can roll over
- the amount of grid usage fee
- the cap to the size of photovoltaic systems eligible for the net metering program
- the type of electric phase eligible for the net metering program
What are the Benefits of Net Metering?
Net metering offers several benefits, including the following:
Indirect Battery Storage: One of the significant pros of hybrid rooftop solar is that it lets homeowners use the public grid as indirect battery storage for excess electricity.
Reduce Electricity Bills: When solar panels produce a surplus of electricity, the net meter records this excess and credits it to the bill as a rooftop solar subsidy.
More Efficient Power Grid: Supporting grid stability and reliability by allowing distributed energy resources to contribute to the electricity supply.
What are the Cons of Net Metering?
Grid Usage Fee: Net metering has two types of costs: a direct one-time payment along with installing solar panels for the home and another permanent but indirect grid usage fee set by the utility provider.
Type of Electric Phase: The power supply is divided into single phase (1-phase) and three-phase (3-phase) where the former can only serve low electricity requirements and the latter carries heavier loads.
Net energy metering helps justify the high cost of installing solar panels for home with equally high Return on Investment (ROI). Join us today to make the country a greener and cleaner space with solar energy.